The only opening for air to enter your lungs is through your nose, making it a crucial component of your respiratory system. As you breathe, it warms and moisturises the air while filtering out small particles. Your nose also provides your sense of smell.
Because the nose exposes mucosal membranes containing immunoglobulin A to inspired air, it serves as the body’s first line of defence against immune system assaults (IgA). The recent, well-publicised COVID-19 pandemic forced us to learn how to prevent infections from getting inside our noses. It encouraged us to purchase a health insurance policy online to cover unexpected medical costs.
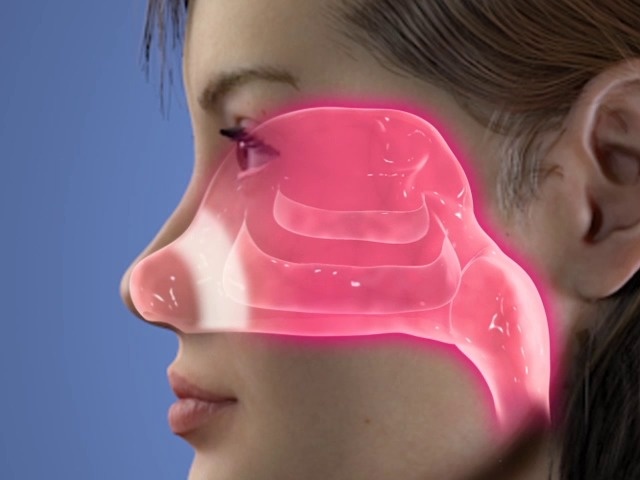
Anatomy of the Nose: Basics
The nose’s internal structure comprises cartilage and bones that shape its external and internal components. The external nose consists of frontal, basal, and lateral regions, with nasal bones supporting the bridge. Key parts of the nose’s anatomy include:
- Nasal Bone: Supports the nose’s bridge, forming part of the facial skeleton.
- Mucous Membrane: Lines the nose, sinuses, and throat, contributing to air moisture and creating mucus to prevent particle entry.
- Nasal Cavities: Hollow areas through which air enters the lungs, divided into two sections.
- Nerve Cells: Olfactory nerves responsible for the sense of smell.
- Nostril: External entrance on the face.
- Septum: Division running through the middle of the nose, separating nasal cavities.
- Sinuses: Air-filled spaces in the skull that produce mucus.
- Turbinates: Tiny structures that purify and humidify inhaled air.
The external nose, resembling a pyramid, comprises cartilaginous and bony components, with distinct features like the nasal root, dorsum, alae nasi, and septum.
Functionality Of The Nose
Understanding the anatomy sets the stage for comprehending the nose’s functionality, which extends beyond essential respiration:
- Inhalation: The nose initiates breathing, with inhaled air travelling through nasal cavities to the lungs.
- Appearance And Sound: The nose influences facial symmetry and contributes to vocal resonance by channelling sound through nasal cavities.
- Air Filtration: Mucus and cilia prevent dust and particles from entering the body.
- Air Moistening And Purification: Cilia humidify inhaled air, and nasal conchae stir the air for optimal humidification.
- Sense Of Smell: Olfactory sensory neurons in the nose provide the ability to smell.
- Sense Of Taste: Olfactory receptors interact with taste buds when chewing food, enhancing the perception of flavour.
The Value Of Health Insurance
The COVID-19 pandemic underscored the importance of health awareness and prompted a surge in online health insurance policy purchases. Health insurance is crucial in managing medical emergencies. Key considerations include understanding individual healthcare needs and exploring online options to reduce premiums. Claims are subject to terms and conditions set forth under the health insurance policy. *
Health insurance policyholders can get benefits of health insurance from several additional features that can help them in difficult circumstances. The cost of care and network hospital stays can be partially covered by a comprehensive medical insurance plan, allowing the patient to concentrate on their quick recovery rather than their financial situation. Make sure you compare health insurance policies before buying one. Claims are subject to terms and conditions set forth under the health insurance policy. *
* Standard T&C Apply
Insurance is the subject matter of solicitation. For more details on benefits, exclusions, limitations, terms, and conditions, please read the sales brochure/policy wording carefully before concluding a sale.